How to Teach Counting On Addition So the Strategy STICKS!
We know that when we teach procedures in math that many of our students lack the ability to generalize those procedures and apply them when it’s appropriate. How often have you heard this description of a struggling student:
“They have great rote procedures but they struggle when it comes to the application”.
1) Link It Back
2) Context Is King
3) Think CRA
Link It Back
Context Is King
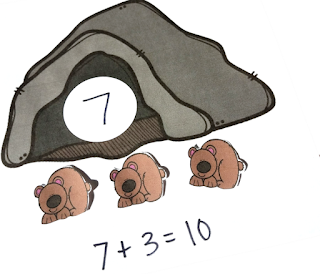 So how do I teach my students to count on without outright stating “We can count on to add parts together. You count on by…”? I give my students a context that lends itself to counting on even though they don’t yet know that strategy!
So how do I teach my students to count on without outright stating “We can count on to add parts together. You count on by…”? I give my students a context that lends itself to counting on even though they don’t yet know that strategy!
In this example, you can see that I have told my students there are 7 bears in the cave and 3 outside. I want them to figure out how many bears there are altogether without ever getting to see the bears inside the cave.
This scenario lends itself perfectly to the counting on strategy. Once my students think they have solved the problem we can get out manipulatives to show 7 bears in the cave and 3 outside and discuss whether or not our counting on strategy was successful in putting the parts together.
Think CRA
 When teaching a new strategy that is more abstract in nature such as counting on, it’s always helpful to think CRA. Concrete, Representative, Abstract.
When teaching a new strategy that is more abstract in nature such as counting on, it’s always helpful to think CRA. Concrete, Representative, Abstract.Concrete: Early in my teaching of the counting on strategy, I start with an activity where I show them a wallet and tell them that there are $6 inside. Outside, there are $5 more. Students can try the counting on strategy but can touch, feel, and manipulate the dollars to solidify their thinking.
Representational: When my students are showing a level of confidence with concrete manipulatives, I would move to a more representative model such as the pictures of the bears in the cave shown above. In this way, our students are able to “trust” that there are a given number of bears in the cave. They are beginning to be comfortable manipulating the numbers without having to physically manipulate the scenario.
Abstract: Ultimately, when teaching counting on or when teaching any variety of other math strategies, you will want your students to be able to perform the strategy given an equation with pencil and paper or mentally. This is the abstract level and is best reinforced once your students have solidified the strategy through concrete and representative means.
Pin For Later:







